What is it?
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa.
Function
Its pH changes very little when a small or moderate amount of strong acid or base is added to it and thus it is used to prevent changes in the pH of a solution.
Use
Many life forms thrive only in a relatively small pH range so they utilize a buffer solution to maintain a constant pH.
pH Calculation
Henderson–Hasselbalch equation
How buffer works
If a strong acid is added to a buffer, the weak base will react with the H+ from the strong acid to form the weak acid HA: H+ + A- → HA. The H+ gets absorbed by the A- instead of reacting with water to form H3O+ (H+), so the pH changes only slightly.
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa.
Its pH changes very little when a small or moderate amount of strong acid or base is added to it and thus it is used to prevent changes in the pH of a solution.
Many life forms thrive only in a relatively small pH range so they utilize a buffer solution to maintain a constant pH.
Applications
Buffer solutions are used...
- to keep the correct pH for enzymes in many organisms to work.
- to maintain a pH between 7.35 and 7.45 in blood plasma (bicarbonate buffering system).
- in fermentation processes and in setting the correct conditions for dyes used in colouring fabrics.
- in chemical analysis and calibration of pH meters.
- in creation of the majority of biological samples that are used in research.
Adjustment
For buffers in acid regions, the pH may be adjusted to a desired value by adding a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid to the buffering agent. For alkaline buffers, a strong base such as sodium hydroxide may be added.
How buffer works
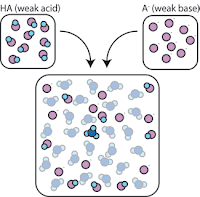
If we mix a weak acid (HA) with its conjugate base (A-), both the acid and base components remain present in the solution.
So, the weak acid and weak base remain in the solution with high concentrations since they only rarely react with the water. However, they are very likely to react with any added strong base or strong acid.
So, the weak acid and weak base remain in the solution with high concentrations since they only rarely react with the water. However, they are very likely to react with any added strong base or strong acid.
If a strong base is added to a buffer, the weak acid will give up its H+ in order to transform the base (OH-) into water (H2O) and the conjugate base: HA + OH- → A- + H2O.
Since the added OH- is consumed by this reaction, the pH will change only slightly.




Comments
Post a Comment